The Java for loop allows the user to iterate a part of the program multiple times. If a user is certain about how many specific numbers of times the loop must be executed then for loop is recommended. It is also an entry-control loop but here flow control contains three steps:
- initialization = The first step is the initialization of the variable and is executed only once. And need to end with a semicolon(;).
- condition = Second is condition check, it checks for a boolean expression. If true then enter the block and if false exit the loop. And need to end with a semicolon(;).
- Increment or Decrement = The third one is the increment or decrement of the variable for the next iteration. Here, we need to use the semicolon(;).
Flowchart of for loop in Java:
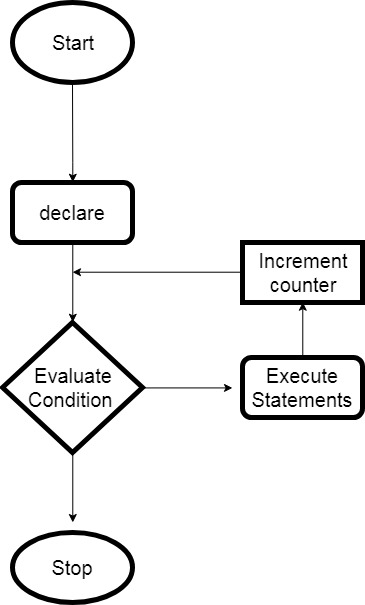
Syntax of for loop:
1 2 3 4 | for(initialization; condition; Increment or Decrement) { // Statements } |
Example of for loop in Java:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | public class ForTest { public static void main(String args[]) { for(int a = 1; a < 10; a++) { System.out.println("value of a : " + a ); } } } |
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | value of a : 1 value of a : 2 value of a : 3 value of a : 4 value of a : 5 value of a : 6 value of a : 7 value of a : 8 value of a : 9 |
