In this post, we will learn how to implement Quick Sort in java. First, we will start by understanding the Quick Sort algorithm.
Quick Sort Algorithm
Quicksort algorithm is a way of rearranging the elements in an array in ascending or descending order. Quicksort is another Divide and Conquer algorithm.
It takes two empty arrays to hold elements, the first is less than the pivot value and the second element greater than the pivot value, and then sort the element around it or inside it. It involves Swapping and partitioning a section of the array.
Time Complexity of Quick Sort:
- Best case:
0(n log n) - Average case:
0(n log n) - Worst case:
0(n^2)
Implementation of Quick sort in java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class QuickSort
{
private static int array[];
public static void Qsort(int[] arr)
{
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0)
{
return;
}
array = arr;
quickSort(0, array.length - 1);
}
private static void quickSort(int left, int right)
{
int i = left;
int j = right;
// finding pivot number
int pivot = array[left + (right - left) / 2];
while (i <= j)
{
//Find element greater than pivot
while (array[i] < pivot)
{
i++;
}
while (array[j] > pivot)
{
j--;
}
if (i <= j)
{
exchange(i, j);
i++;
j--;
}
}
// recursssive
if (left < j)
quickSort(left, j);
if (i < right)
quickSort(i, right);
}
private static void exchange(int i, int j)
{
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
public static void main(String a[])
{
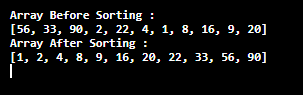
int[] arr = { 56, 33, 90, 2, 22, 4, 1, 8, 16, 9, 20 };
System.out.println("Array Before Sorting : ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
Qsort(arr);
System.out.println("Array After Sorting : ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}The output of Quicksort algorithm in java: